Materials engineers design and develop new materials to enable the technology of tomorrow. They use metals, composites, ceramics, and plastics to create materials which meet specific chemical, mechanical, and electrical requirements.
What does a materials engineer do?
Material engineers test, develop, and process the raw materials that are used in a variety of products, such as computer chips, golf clubs, or biomedical devices. These engineers evaluate and study the properties and structures of metals such as ceramics or plastics. They also examine nanomaterials which are extremely small substances.
Materials engineers' responsibilities vary depending on the type of material they work with and the sector in which they work. However, they are often responsible for assessing production costs, quality control, creating budgets, and supervising technicians.
What is a Materials Science Engineer?
Materials science engineers work with different materials, such as metals, composites, ceramics and ceramics to make them lighter, stronger and more durable. They can develop new materials and improve existing ones.
What do materials engineers need?
A bachelor's in engineering or materials sciences is required to become a material engineer. The degree program should emphasize engineering principles in the classroom and lab. The program can be completed in a few short years.
After graduation you can get a job as materials engineer and you will earn around PS25,000 each year. As you gain more experience, your salary will increase.
How to become a material engineer
Qualifications for materials engineers vary depending on the industry and employer. However, most jobs require at least a bachelor's degree in materials science or engineering. This will involve studies in chemistry, math, and physics.
A materials science engineer's qualifications are usually a high school diploma, and a bachelor degree in an appropriate field like physics or chemistry. For higher-level positions in research, a master's degree or doctoral qualification is often required.
How much money can I make as a materials engineer?
Salary of materials engineers may vary depending on the level of their expertise, the sector in which they are employed and the size of their company. Other perks and bonuses can be expected for their work.
What will the future look like for the Materials Engineering career?
Careers in materials engineering are expected to grow rapidly, as many new job opportunities will open up to those who pursue them. This is because of the increasing demand for newer, more advanced materials in fields such as medicine, architecture and communication.
By obtaining a degree, you can become a materials engineering. You may choose to study metallurgy. chemistry or physics. This will give you the knowledge you need to pursue a career in this industry and may open up more opportunities for you down the line. A degree in an area such as Chemistry will improve your skills for research and innovation. You can gain more experience by working in an engineering firm specializing in specific fields of materials.
FAQ
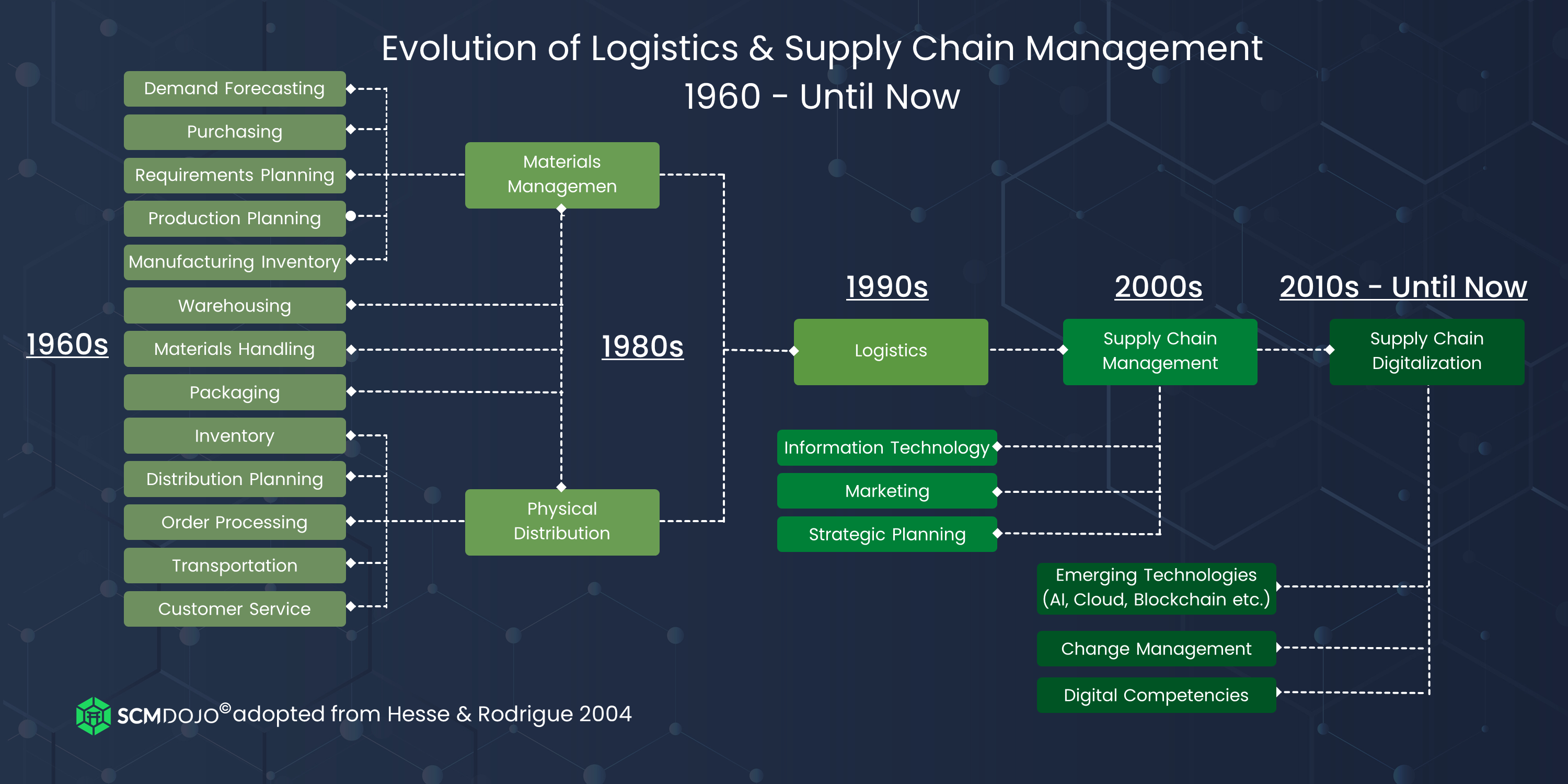
What are the products and services of logistics?
Logistics is the process of moving goods from one point to another.
They include all aspects of transport, including packaging, loading, transporting, unloading, storing, warehousing, inventory management, customer service, distribution, returns, and recycling.
Logisticians make sure that the right product arrives at the right place at the correct time and in safe conditions. They help companies manage their supply chain efficiency by providing information on demand forecasts, stock levels, production schedules, and availability of raw materials.
They monitor shipments in transit, ensure quality standards, manage inventories, replenish orders, coordinate with suppliers and other vendors, and offer support services for sales, marketing, and customer service.
What are the jobs in logistics?
There are many kinds of jobs available within logistics. Some examples are:
-
Warehouse workers: They load and unload trucks, pallets, and other cargo.
-
Transportation drivers – They drive trucks or trailers to transport goods and perform pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers are people who sort and pack freight into warehouses.
-
Inventory managers - These are responsible for overseeing the stock of goods in warehouses.
-
Sales reps - They sell products and services to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They organize and plan logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents are those who purchase goods and services for the company.
-
Customer service representatives – They answer emails and phone calls from customers.
-
Shipping clerks - They process shipping orders and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - These people fill orders based on what has been ordered.
-
Quality control inspectors – They inspect incoming and outgoing products to ensure that there are no defects.
-
Others - There is a variety of other jobs in logistics. These include transportation supervisors and cargo specialists.
What is the difference between a production planner and a project manager?
The primary difference between a producer planner and a manager of a project is that the manager usually plans and organizes the whole project, while a production planner is only involved in the planning stage.
Statistics
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to use the Just-In Time Method in Production
Just-in time (JIT), is a process that reduces costs and increases efficiency in business operations. This is where you have the right resources at the right time. This means you only pay what you use. The term was first coined by Frederick Taylor, who developed his theory while working as a foreman in the early 1900s. He saw how overtime was paid to workers for work that was delayed. He realized that workers should have enough time to complete their jobs before they begin work. This would help increase productivity.
JIT is about planning ahead. You should have all the necessary resources ready to go so that you don’t waste money. It is important to look at your entire project from beginning to end and ensure that you have enough resources to handle any issues that may arise. You can anticipate problems and have enough equipment and people available to fix them. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This is a type of JIT where you order the parts/materials needed for your project regularly. This will let you track the amount of material left over after you've used it. This will allow to you estimate the time it will take for more to be produced.
-
Inventory-based: This is a type where you stock the materials required for your projects in advance. This allows one to predict how much they will sell.
-
Project-driven: This approach involves setting aside sufficient funds to cover your project's costs. When you know how much you need, you'll purchase the appropriate amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT: This type of JIT is most commonly used. You assign certain resources based off demand. You will, for example, assign more staff to deal with large orders. You'll have fewer orders if you have fewer.
-
Cost-based: This approach is very similar to resource-based. However, you don't just care about the number of people you have; you also need to consider how much each person will cost.
-
Price-based: This is very similar to cost-based, except that instead of looking at how much each individual worker costs, you look at the overall price of the company.
-
Material-based: This is very similar to cost-based but instead of looking at total costs of the company you are concerned with how many raw materials you use on an average.
-
Time-based JIT: A variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing solely on the amount each employee costs, focus on how long it takes for the project to be completed.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about the cost of each employee or the time it takes to produce something, you focus on how good your product quality.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. This is where you don't care about how the products perform or whether they meet customers' expectations. Instead, your goal is to add value to the market.
-
Stock-based. This method is inventory-based and focuses only on the actual production at any given point. It's useful when you want maximum production and minimal inventory.
-
Just-in time (JIT), planning: This is a combination JIT/supply chain management. It's the process of scheduling delivery of components immediately after they are ordered. It reduces lead times and improves throughput.