
Thousands of Connecticut manufacturing jobs are waiting to be filled. There are 411 manufacturers in Connecticut that employ 159,000 people. Manufacturing is the biggest contributor to the Gross State Product of Connecticut and provides a high-paying job for its workers. The Connecticut Business and Industry Association recently released a survey of manufacturing workforce needs. They found that 13,000 manufacturing jobs are unfilled in the state, with many companies struggling to hire younger workers.
Connecticut's manufacturing workforce tends to be older with one-third of its workers over 55. To reduce labor costs, many companies moved manufacturing plants. Other operations started using new machinery and automation. Although manufacturing used to be considered hazardous and dirty in the past it has gained a better reputation. Today, companies offer apprenticeships, internships, and entry level positions. Manufacturing is Connecticut’s third largest employment sector. Its high tech operations are a key competitive advantage.
Connecticut offers a variety of programs that can help individuals become skilled in manufacturing. The Manufacturing Innovation Fund is a program that supports high schools, universities, vocational high schools, and comprehensive high schools. It also supports online training, pre-apprenticeships, career activities, and career activities, for K-12 students.

Many backgrounds go into becoming advanced manufacturing workers. Some work in manufacturing right out of highschool while others have worked in different fields for many years before switching to the field. They may have left school to earn a degree, or they may have entered the workforce after years of service in the military. Many companies will offer tuition assistance for advanced manufacturing and wage subsidies for entry-level programs.
The state's Comprehensive High Schools have also begun reintroducing technical education options. The Grasso Tech welding program, which will be starting in fall 2019, is one example. Employers that employ students through the EB may be interested to hire Connecticutans. The Eastern Connecticut Manufacturing Pipeline provides support to advanced manufacturing firms in the region. It is modeled after Eastern Connecticut Workforce Investment Board’s Manufacturing Pipeline.
The Manufacturing Careers Program was created to assist job seekers interested in manufacturing careers and demonstrate their readiness for entry-level work. It connects pre-screened job applicants with manufacturers and other employers. The program offers a CNC Basics training course as well as a career path that is industry-focused. Those enrolled in the program may also join the Advanced Manufacturing Employer Partnership, which offers wage subsidies for entry level training.
Young people entering the workforce may not be aware of the manufacturing industry, or may not want to pursue a career in manufacturing. This lack of awareness may make it difficult for them to participate in these education programs. These programs are funded by the state with millions of dollars. Because young people don't know these jobs exist, those programs have a limited impact.
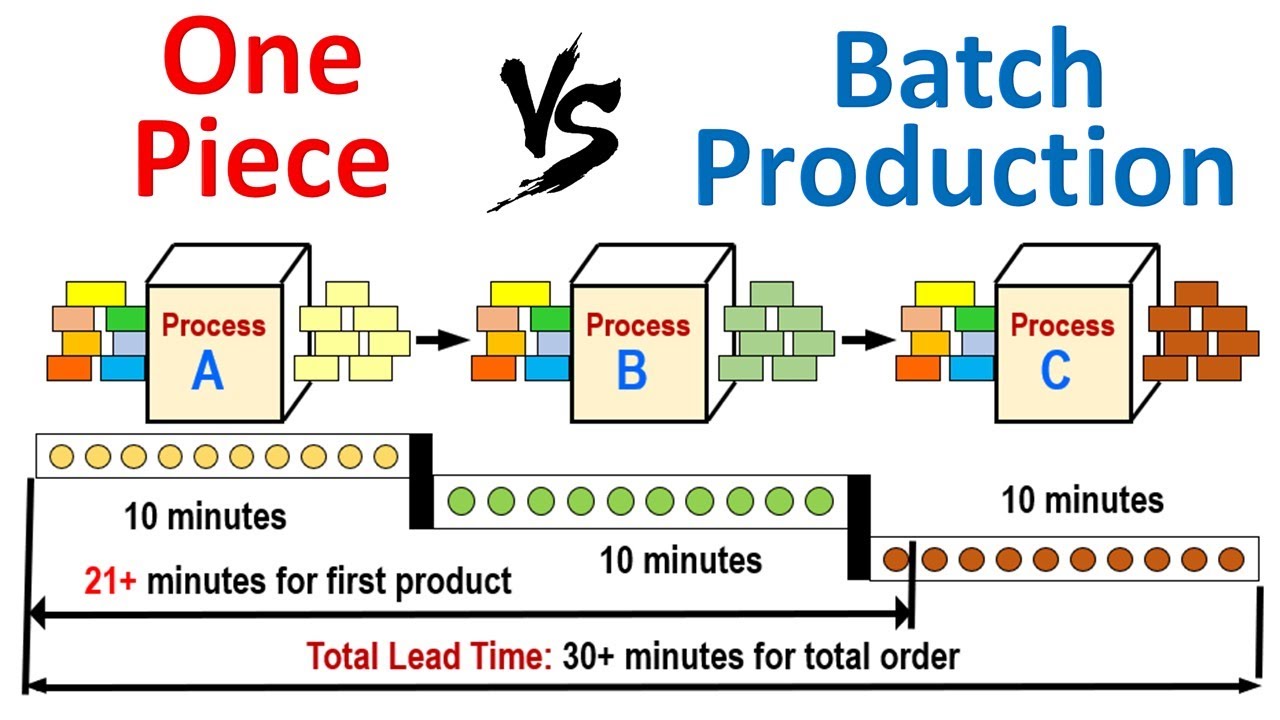
A state-wide STEM Town initiative is an innovative solution to Connecticut's manufacturing job shortage. This would mean reallocating resources, improving education programs and meeting the needs manufacturers.
FAQ
What is the difference between Production Planning, Scheduling and Production Planning?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. This is accomplished by forecasting the demand and identifying production resources.
Scheduling is the process of assigning specific dates to tasks so they can be completed within the specified timeframe.
What does manufacturing industry mean?
Manufacturing Industries refers to businesses that manufacture products. These products are sold to consumers. To accomplish this goal, these companies employ a range of processes including distribution, sales, management, and production. These companies produce goods using raw materials and other equipment. This includes all types manufactured goods such as clothing, building materials, furniture, electronics, tools and machinery.
Are there any Manufacturing Processes that we should know before we can learn about Logistics?
No. No. But, being familiar with manufacturing processes will give you a better understanding about how logistics works.
What type of jobs is there in logistics
There are many types of jobs in logistics. Here are some:
-
Warehouse workers – They load and unload pallets and trucks.
-
Transportation drivers – They drive trucks or trailers to transport goods and perform pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers, - They sort out and pack freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers - These are responsible for overseeing the stock of goods in warehouses.
-
Sales reps are people who sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents - They buy goods and services that are necessary for company operations.
-
Customer service representatives - They answer calls and emails from customers.
-
Shipping clerks - They process shipping orders and issue bills.
-
Order fillers: They fill orders based off what has been ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors: They inspect outgoing and incoming products for any defects.
-
Others – There are many other types available in logistics. They include transport supervisors, cargo specialists and others.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics?
The 7R's of Logistics is an acronym for the seven basic principles of logistics management. It was developed and published by the International Association of Business Logisticians in 2004 as part of the "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The following letters make up the acronym:
-
Responsible - ensure that all actions taken are within legal requirements and are not harmful to others.
-
Reliable: Have faith in your ability or the ability to honor any promises made.
-
Be responsible - Use resources efficiently and avoid wasting them.
-
Realistic – Consider all aspects, including cost-effectiveness as well as environmental impact.
-
Respectful - show respect and treat others fairly and fairly
-
Reliable - Find ways to save money and increase your productivity.
-
Recognizable is a company that provides customers with value-added solutions.
Why automate your warehouse?
Modern warehousing has seen automation take center stage. E-commerce has increased the demand for quicker delivery times and more efficient processes.
Warehouses should be able adapt quickly to new needs. In order to do this, they need to invest in technology. Automating warehouses is a great way to save money. Here are some of the reasons automation is worth your investment:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Accuracy is improved
-
Boosts safety
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale up more easily
-
This makes workers more productive
-
Gives you visibility into all that is happening in your warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reduces downtime and improves uptime
-
This ensures that quality products are delivered promptly
-
Removing human error
-
It helps ensure compliance with regulations
Statistics
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma is defined as "the application of statistical process control (SPC) techniques to achieve continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department, Tokyo, Japan, developed it in 1986. The basic idea behind Six Sigma is to improve quality by improving processes through standardization and eliminating defects. Many companies have adopted Six Sigma in recent years because they believe that there are no perfect products and services. Six Sigma's primary goal is to reduce variation from the average value of production. This means that if you take a sample of your product, then measure its performance against the average, you can find out what percentage of the time the process deviates from the norm. If this deviation is too big, you know something needs fixing.
Understanding the nature of variability in your business is the first step to Six Sigma. Once you have a good understanding of the basics, you can identify potential sources of variation. This will allow you to decide if these variations are random and systematic. Random variations occur when people do mistakes. Symmetrical variations are caused due to factors beyond the process. You could consider random variations if some widgets fall off the assembly lines. It would be considered a systematic problem if every widget that you build falls apart at the same location each time.
Once you have identified the problem, you can design solutions. That solution might involve changing the way you do things or redesigning the process altogether. Once you have implemented the changes, it is important to test them again to ensure they work. If they fail, you can go back to the drawing board to come up with a different plan.